Jwt
JWT - JSON Web Token
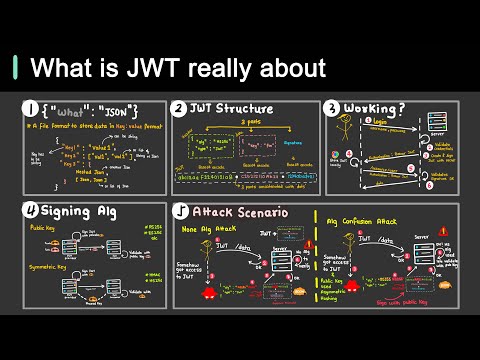
JWT stands for JSON Web Token. It is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims between two parties. JWTs are commonly used to secure the transmission of information between parties in a web environment, typically for authentication and information exchange. The JWT specification is defined by RFC 75191 and it is a decentralized approach for security (which can support horizontal scalability).
Here are the key components and concepts of JWT:
- JSON Format: JWTs are represented as JSON objects that are easy to parse and generate. The JSON format makes them human-readable and easy to work with.
-
Three Parts: JWTs consist of three parts separated by dots (
.): Header, Payload, and Signature.-
Header: The header typically consists of two parts: the type of the token (JWT) and the signing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.
-
Payload: The payload contains the claims. Claims are statements about an entity (typically, the user) and additional data. There are three types of claims: registered, public, and private claims.
-
Signature: To create the signature part, you take the encoded header, the encoded payload, a secret, the algorithm specified in the header, and sign that.
-
-
Encoding: Each of the three parts is Base64Url encoded, and the resulting strings are concatenated with periods between them. The final JWT looks like:
xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzz. - Stateless and Self-contained: JWTs are stateless, meaning that all the information needed is within the token itself. The server doesn't need to store the user's state. They are also self-contained, meaning that all the information needed is contained within the token.
- Use Cases: JWTs are commonly used for authentication and information exchange between parties. For example, after a user logs in, a server could generate a JWT and send it to the client. The client can then include the JWT in the headers of subsequent requests to access protected resources. The server can verify the authenticity of the JWT using the stored secret key.
- Security Considerations: While JWTs are widely used and versatile, it's important to handle them securely. For instance, the key used to sign the JWT should be kept secret, and HTTPS should be used to transmit JWTs to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Here's a simple example of a JWT created on JWT Builder2:
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiJJbnNwZXIiLCJpYXQiOjE3MDMwMDgzMzgsImV4cCI6MjAxODU0MTEzOCwiYXVkIjoid3d3Lmluc3Blci5lZHUuYnIiLCJzdWIiOiJodW1iZXJ0b3JzQGluc3Blci5lZHUuYnIiLCJHaXZlbk5hbWUiOiJIdW1iZXJ0byIsIlN1cm5hbWUiOiJTYW5kbWFubiIsIkVtYWlsIjoiaHVtYmVydG9yc0BpbnNwZXIuZWR1LmJyIiwiUm9sZSI6IlByb2Zlc3NvciJ9.SsGdvR5GbYWTRbxY7IGxHt1vSxhkpRueBJWsi0lrPhJVCICp119QjU8F3QvHW0yF5tw-HhQ9RVh0l89t4M0LNw
This JWT consists of three parts, decoded by 3:
eyJpc3MiOiJJbnNwZXIiLCJpYXQiOjE3MDMwMDgzMzgsImV4cCI6MjAxODU0MTEzOCwiYXVkIjoid3d3Lmluc3Blci5lZHUuYnIiLCJzdWIiOiJodW1iZXJ0b3JzQGluc3Blci5lZHUuYnIiLCJHaXZlbk5hbWUiOiJIdW1iZXJ0byIsIlN1cm5hbWUiOiJTYW5kbWFubiIsIkVtYWlsIjoiaHVtYmVydG9yc0BpbnNwZXIuZWR1LmJyIiwiUm9sZSI6IlByb2Zlc3NvciJ9
JWTs are widely used in web development due to their simplicity, flexibility, and support across various programming languages and frameworks. They are commonly used in token-based authentication systems.
Addtional Material
-
RFC 7519 - JSON Web Token (JWT), 2015. ↩
-
DELANTHA, R., Spring Cloud Gateway security with JWT, 2023. ↩
-
PGzlan, Serve your hash with Salt and Pepper for Stronger Account Security, 2023. ↩